Maple trees A forester would like to know how big a maple tree might be at age 50 years.
She gathers data from some trees that have been cut down, and plots the diameters (in
inches) of the trees against their ages (in years). First she makes a linear model. The scatterplot and residuals plot are shown. 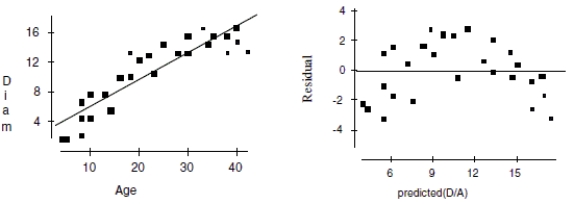
a. Describe the association shown in the scatterplot.
b. Do you think the linear model is appropriate? Explain.
c. If she uses this model to try to predict the diameter of a 50-year old maple tree, would you expect that estimate to be fairly accurate, too low, or too high? Explain.
Now she re-expresses the data, using the logarithm of age to try to predict the diameter of the tree. Here are the regression analysis and the residuals plot.
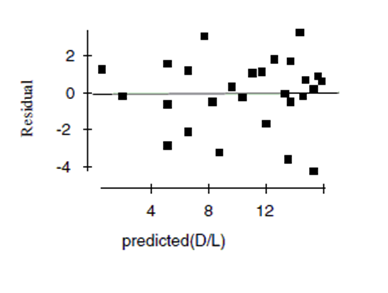
d. Explain why you think this is a better model.
e. Using this model, predict the diameter of a maple tree at age 50 years.
Definitions:
Business Risk
Variation in a company’s financial performance caused by changes in business conditions.
Operating Leverage
A financial ratio that measures the degree to which a firm or project can increase operating income by increasing revenue, highlighting the impact of fixed costs on profits.
Fixed Costs
Expenses that do not change with the level of goods or services produced by a business over a certain period.
Operating Leverage
A financial ratio that measures the proportion of fixed costs to variable costs in a company's cost structure, indicating how revenue growth translates into growth in operating income.
Q4: Not every applicant is eligible.<br>A) (∃x)(Ax •
Q4: Morgan discovers 6 acquaintances who bought Goodmonth
Q10: According to Thomas Kuhn, one feature that
Q13: What cause is suggested by the information
Q14: Which of the following is NOT a
Q29: Judy buys the same model dishwasher as
Q32: Create and interpret a 90% confidence interval.
Q47: UFOs. A National Geographic survey in
Q68: A typical 'public' company has many types
Q89: Which is true about a 98% confidence