The bigger the stop sign, the more expensive it is. Here is a graph of the height of a sign in inches versus its cost in dollars.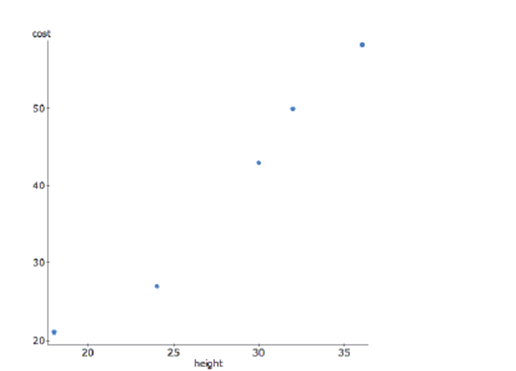
To achieve linearity, the data was transformed using a square root function of cost. Here are the results and a residual plot.Dependent Variable: sqrt(cost)
(correlation coefficient)
s: 0.2141

-Use your equation to predict the cost of a 48" stop sign.
Definitions:
Left Hemisphere
The left side of the human brain, generally associated with analytical and logical thinking processes, including language, number skills, and reasoning.
Right Hand
The dominant hand for the majority of people, often associated with manual tasks and writing.
Corpus Callosum
A substantial cluster of nerve fibers that links the two halves of the brain, enabling the hemispheres to exchange information.
Name
A word or set of words by which a person, place, or thing is known, addressed, or referred to.
Q1: The hypotheses leading to the discovery of
Q6: One of the functions of a hypothesis
Q7: Which of these random variables is most
Q13: Car reliability A consumer group assigned
Q18: Morgan discovers 6 acquaintances who bought Goodmonth
Q25: How many degrees of freedom are there
Q34: One of the problems with the Literary
Q86: R-sq is a measure of ……<br>A) the
Q88: One thousand students from a local university
Q92: Which type of plot would be least