Table 3-4
Assume that the farmer and the rancher can switch between producing meat and producing potatoes at a constant rate.
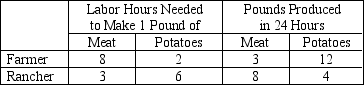
-Refer to Table 3-4.Without trade,the farmer produced and consumed 2 pounds of meat and 4 pounds of potatoes and the rancher produced and consumed 4 pounds of meat and 2 pounds of potatoes.Then,each person agreed to specialize in the production of the good in which they have a comparative advantage and trade 3 pounds of meat for 6 pounds of potatoes.As a result,the farmer gained
Definitions:
Small Business
An independently owned and operated company with limited size and revenue, according to industry standards, often characterized by a small workforce.
Independently Owned
Businesses or properties that are owned by individuals or private entities rather than corporations or chains.
Franchise
A business arrangement where one party (the franchisor) grants another party (the franchisee) the right to use its trademark or business model to offer, sell, or distribute goods or services.
Necessity-based Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurial activities initiated as a result of limited job opportunities or economic necessity, rather than from the identification of a new business opportunity.
Q1: Refer to Table 3-1.Relative to the farmer,the
Q43: Refer to Figure 2-14.Points A,B,and D represent
Q50: Refer to Table 3-7.Japan's opportunity cost of
Q105: International trade may make some individuals in
Q116: Refer to Table 3-2.Aruba should export<br>A) coolers
Q162: Suppose Jim and Tom can both produce
Q182: Refer to Table 3-6.Which of the following
Q217: Refer to Table 3-5.The opportunity cost of
Q299: President Ronald Reagan once joked that a
Q325: Refer to Table 3-17 France has an