Table 10-5
The following table shows the marginal costs for each of four firms (A, B, C, and D) to eliminate units of pollution from their production processes. For example, for Firm A to eliminate one unit of pollution, it would cost $54, and for Firm A to eliminate a second unit of pollution it would cost an additional $67. 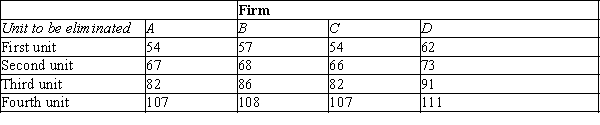
-Refer to Table 10-5. If the government wanted to reduce pollution from 16 units to 6 units, which of the following fees per unit of pollution would achieve that goal?
Definitions:
Square Root Property
A principle stating that for any positive number x, there exists a positive and negative value whose square equals x.
Square Root Property
Refers to a principle used to solve quadratic equations, stating that if \( x^2 = a \), then \( x \) is equal to both the positive and negative square root of \( a \).
Complex Solutions
Solutions to equations that include imaginary numbers, typically used when solving polynomial equations that do not have real-number solutions.
Real Solutions
The solutions of an equation that are real numbers, as opposed to imaginary or complex numbers.
Q15: If only a few people are affected
Q143: Because of the free-rider problem,<br>A) private markets
Q169: Refer to Figure 10-13.If 325 units of
Q170: When a country abandons a no-trade policy,adopts
Q189: Refer to Figure 9-17.When the country moves
Q257: Two firms,A and B,each currently dump 50
Q262: Why is the commercial value of ivory
Q281: The Coase theorem asserts that private economic
Q373: Cost-benefit analysis is important to determine the
Q400: Economists believe that the optimal level of