Table 15-8
The following table provides information on the price, quantity, and average total cost for a monopoly. 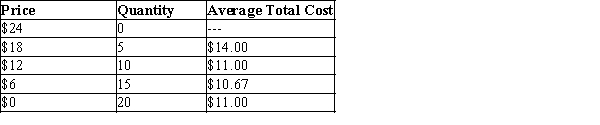
-Refer to Table 15-8. How much extra revenue does the monopolist earn when he lowers the price from $18 to $12?
Definitions:
Joint Cost
Costs incurred in the process of producing two or more products simultaneously from the same raw materials or process, where the costs cannot be separately identified.
Relative Sales Value Method
A technique used to allocate joint costs based on the proportionate sales value of each product produced from a common process.
Joint Cost
The costs incurred in the process of producing two or more products simultaneously, where such costs cannot be separately identified with individual products.
By-Products
Secondary products that are generated alongside the main product during the manufacturing process.
Q57: Suppose a profit-maximizing monopolist faces a constant
Q124: With no price discrimination,the monopolist sells every
Q137: Refer to Figure 15-3.The marginal revenue curve
Q192: Refer to Figure 16-2.Which of the following
Q200: Refer to Figure 14-2.If the market price
Q232: When a restaurant stays open for lunch
Q248: For a monopoly,marginal revenue is often greater
Q321: A patent gives a single person or
Q378: When an individual firm in a competitive
Q422: Refer to Figure 15-6.A profit-maximizing monopolist would