Suppose that a firm's production function is given by Q = KL (MPK = L and MPL = K), where Q is quantity of output, K is units of capital, and L is units of labor. The price per unit of labor and capital are $30 and $20, respectively. 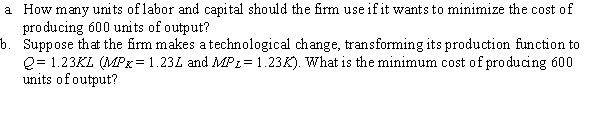
Definitions:
Pure Monopoly
A market structure where a single seller controls the entire market for a particular good or service, with no close substitutes.
Fair-return Price
A price that allows a company to cover its costs and make a reasonable profit.
Short Run
A period in economics where at least one input is considered fixed in the production process.
Natural Monopoly
A market condition where a single firm can provide a good or service at a lower cost than any potential competitor, often due to economies of scale.
Q38: Which of the following factors influences demand?
Q41: Suppose the wage rate is $25 per
Q49: Suppose that the market demand curve for
Q51: Wade Company estimates the cost of
Q59: (Figure 4.1) Sam's grandmother, who is visiting
Q65: A firm that can affect the price
Q87: (Figure 8.7) If the market price is
Q95: Suppose that there are two goods, X
Q96: (Figure 3.4) The outward shift of the
Q100: Suppose that a furniture manufacturer produces tables.