Use synthetic division to divide. 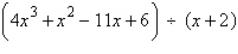
Definitions:
Outcome Goals
Objectives an organization or individual aims to achieve as a result of its activities, focusing on the end results or impacts.
Federal Grant Programs
Government initiatives that provide financial support to individuals, institutions, or governments for a specific purpose, often to fund projects or research.
Organizational Autonomy
The degree to which an organization can set its own policies and make decisions without external control.
Block Grants
A form of financial aid from a central government to a regional or local authority which can be used at the discretion of the recipient for a wide range of purposes within broad categories.
Q1: Describe the right-hand and the left-hand behavior
Q1: Evaluate <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4588/.jpg" alt="Evaluate when
Q9: A firm in a perfectly competitive industry<br>A)
Q17: Given <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4588/.jpg" alt="Given ,
Q26: Suppose that capital costs $6 per unit
Q36: With regard to economic decision making for
Q37: Simplify the given expression algebraically. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4588/.jpg"
Q41: In the long run, a profit-maximizing firm
Q58: Consumer surplus is<br>A) the same as total
Q68: Solve for X in the equation given.