The diagram below shows the demand and supply curves in a perfectly competitive market. 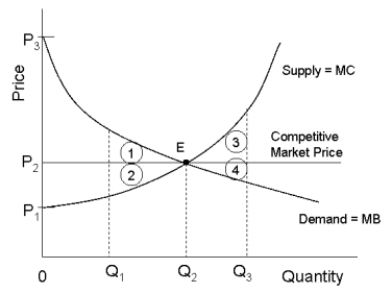 FIGURE 12-5
FIGURE 12-5
-Refer to Figure 12-5. If output in this market were Q₃, and the price was still equal to itsfree-market level, the loss in producer surplus relative to the competitive equilibrium would be illustrated by area
Definitions:
Temporal Lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the brain, associated with processing auditory information and encoding memory.
Thalamus
A major part of the brain that acts as a relay station, transmitting information from the sensory organs to the cerebral cortex.
Fast Pathway
A term that may refer to a rapid signaling route within the nervous system, especially in the context of pain perception.
Endorphins
Natural chemicals in the body that interact with the brain's receptors to reduce pain and boost pleasure, resulting in a feeling of well-being.
Q8: Consider a monopolist that is able to
Q17: A natural monopoly<br>A) generally needs to be
Q33: Refer to Figure 6-7. The movement of
Q37: Allocative efficiency is a property of the
Q45: Which statement best describes the "law of
Q48: In a monopolistically competitive industry, the freedom
Q49: Refer to Table 2-2. Assume that 2005
Q50: The market supply curve for wooden shipping
Q83: If the demand for some good fluctuates,
Q85: A company purchases property that includes land,