The diagram below shows the market demand curve and the cost curves for a single firm. 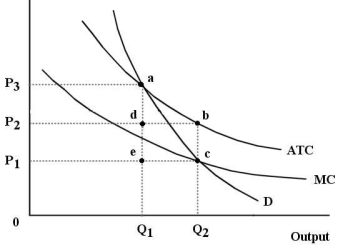 FIGURE 12-6
FIGURE 12-6
-Refer to Figure 12-6. Suppose this firm is a government-owned natural monopoly and imposes a price so as to achieve allocative efficiency in this market. The amount of tax revenue that the government must raise elsewhere in the economy to offset the losses of this firm is represented by the area
Definitions:
Subjective Assessment
An evaluation based on personal judgment rather than quantifiable evidence, often used in scenarios where objective measures are difficult to apply.
Deferred Tax Assets
Future tax benefits obtained due to temporary differences between the book value and tax basis of assets.
Deferred Tax Liabilities
Obligations for taxes owed in the future due to temporary differences between the tax basis of an asset or liability and its reported amount in the financial statements.
Book Income Tax Expense
The amount of income tax a company reports in its financial statements, which may differ from the tax owed to tax authorities.
Q22: The Canadian economy is achieving allocative efficiency
Q28: For a single-price monopolist, marginal revenue falls
Q34: Consider an example of the prisoner's dilemma
Q44: The right to exclude others from making
Q48: The statement that a country's rate of
Q70: Refer to Table 2-1. The increase in
Q78: To say that the demand curve for
Q79: The demand curve facing a monopolistically competitive
Q85: According to economist George Stigler, the process
Q108: What is the adjusted balance in the