SCENARIO 13-9
It is believed that, the average numbers of hours spent studying per day (HOURS) during undergraduate education should have a positive linear relationship with the starting salary (SALARY, measured in thousands of dollars per month) after graduation. Given below is the Excel output for predicting starting salary (Y) using number of hours spent studying per day (X) for a sample of 51 students. NOTE: Only partial output is shown.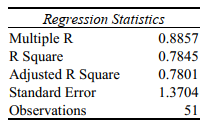
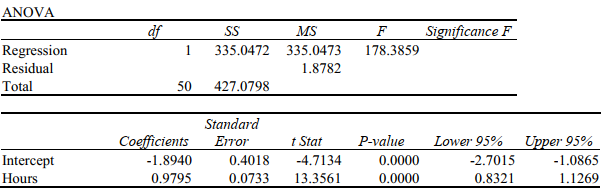
Note: 2.051 E - 05 = 2.051*10-5 and 5.944 E -18 = 5.944 *10 -18 .
-Referring to Scenario 13-9,the p-value of the measured F-test statistic to test whether HOURS affects SALARY is .
Definitions:
Planning Gap
The difference between an organization's current position and its desired future state, identified during strategic planning.
Contribution Margin
The amount by which product or service sales exceed variable costs, contributing to covering fixed costs and profit generation.
Planning Gap
The difference between future desired performance and projected actual performance, identified during strategic planning processes.
Sales Revenue Data
Information regarding the income generated from the sale of goods or services before any expenses are subtracted.
Q37: Referring to Scenario 11-3,using an overall level
Q55: Referring to Scenario 11-8,it is appropriate to
Q63: Which of the following assumptions concerning the
Q85: Referring to Scenario 13-7,to test whether
Q89: Referring to Scenario 14-5,what is the p-value
Q136: Referring to Scenario 11-6,the randomized block F
Q146: Referring to Scenario 16-3,if this series is
Q160: Referring to Scenario 11-4,the null hypothesis should
Q212: Referring to Scenario 14-17,what are the lower
Q237: Referring to Scenario 14-2,for these data,what is