Find the critical point(s) of the function.Then use the second derivative test to classify the nature of each point, if possible.Finally, determine the relative extrema of the function. 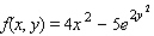
Definitions:
ROE
Return on Equity (ROE) is a measure of a corporation's profitability that reveals how much profit a company generates with the money shareholders have invested.
EPS
Earnings Per Share, a company's profit divided by the number of outstanding shares of its common stock.
Equity Multiplier
A financial leverage ratio that measures the portion of a company's assets that are financed by stockholder's equity.
Degree Of Total Leverage
A measure that quantifies the sensitivity of a company's earnings before interest and taxes to a change in its sales.
Q9: Portfolio selection problems should acknowledge both risk
Q10: Which of the following statements is INCORRECT
Q20: A company seeks to maximize profit subject
Q126: Find the indefinite integral. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7866/.jpg" alt="Find
Q140: Evaluate the given definite integral. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7866/.jpg"
Q188: Find the average value of the function
Q207: A state lottery commission pays the winner
Q215: Find the indefinite integral. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7866/.jpg" alt="Find
Q227: The life span (in years) of a
Q237: Find the area of the region bounded