At a temperature of 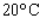 , the volume V (in liters) of 1.33 g of
, the volume V (in liters) of 1.33 g of 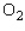 is related to its pressure p (in atmospheres) by the formula
is related to its pressure p (in atmospheres) by the formula 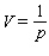 .
.
What is the average rate of change of V with respect to p as p increases from 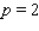 to
to 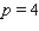 ? What is the rate of change of V with respect to p when
? What is the rate of change of V with respect to p when 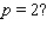
Definitions:
Degree Of Oligopolization
The extent to which a market or industry is dominated by a few large companies, limiting competition.
Collusion
An agreement between competing firms to control prices or exclude entry of a new competitor in the market, often in secret, to reduce competition and increase profitability.
Cutthroat Competition
An intense form of competition in a market where competitors aggressively undercut each other's prices or use other aggressive tactics to gain market share.
Concentration Ratios
Measures that indicate the extent to which a small number of firms dominate an industry or market.
Q16: An employer is obligated to verify the
Q48: The 1980s saw a trend toward old-fashioned
Q172: If the line passing through the points
Q180: Find the limit. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7866/.jpg" alt="Find the
Q192: The volume of a spherical cancerous tumor
Q197: Factor the expression. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7866/.jpg" alt="Factor the
Q198: Find the limit, if it exists. <img
Q269: Find the derivative of the function. <img
Q307: A certain country's government economists have determined
Q329: A division of Ditton Industries manufactures the