(This problem illustrates the computation of beta coefficients may be solved using a statistics program or Excel.) The returns on the market and stock A and stock B are as follows: 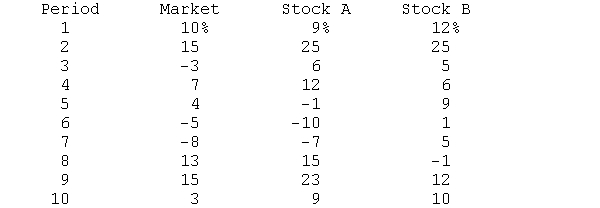 Compute the beta coefficient for each stock and interpret the results of the computations.
Compute the beta coefficient for each stock and interpret the results of the computations.
Definitions:
Compounding Periods
The frequency with which interest is added to the principal balance of an investment, affecting the total interest earned.
Future Value
The value of an investment or a sum of money projected to grow over a specified period of time, often calculated using the interest rate.
Present Value
Present value is the current worth of a future sum of money or stream of cash flows given a specified rate of return, used in time value of money calculations to compare investment options.
Amortized Loan
A loan with scheduled periodic payments that consist of both principal and interest, so the loan is paid off by the end of the term.
Q3: The FIFO method leads to a higher
Q8: The objective of Sarbanes-Oxley was to create
Q22: A global fund invests solely in foreign
Q25: The S&P 500 uses<br>A) a simple average<br>B)
Q33: An active portfolio strategy is premised on<br>A)
Q41: The SEC establishes the price of a
Q41: Even though Firm A's current ratio exceeds
Q66: Mutual funds with beta coefficients greater than
Q106: You want to accumulate $2,500,000 in your
Q106: It is appropriate to use the fixed