In a study of the effects of rewards on learning in rats, an experimenter divided 20 rats into 4 groups of equal sizes. Each rat was run through a maze, and there was only one correct method of exiting the maze. The rats were rewarded on different schedules. The investigators observed the number of trials it took the rats to learn the maze.
Group A: The rats were rewarded for every correct direction chosen in the maze
Group B: The rats were randomly rewarded 75% of the time
Group C: The rats were randomly rewarded 25% of the time
Group D: The rats were not rewarded at all.
The following table contains summary information for this experiment. 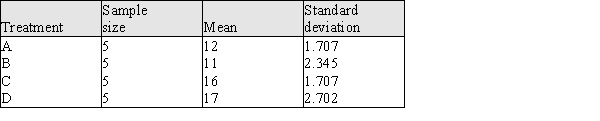
a) Construct the appropriate ANOVA table and test the hypothesis that there is no difference between the mean number of trials needed to learn the maze for the different reward treatments.
b) Is there evidence that the 25% random reward schedule and the 75% random reward schedule result in a different mean number of trials to learn the maze? Give statistical evidence to support your answer.
Definitions:
Medical Laboratory Scientists
Professionals who conduct laboratory tests and procedures to diagnose diseases and provide data for treatment by physicians.
Nuclear Medicine Technologists
Nuclear Medicine Technologists are healthcare professionals who specialize in preparing and administering radioactive drugs for imaging or therapeutic purposes, and they operate devices that detect and map the radioactive drug in a patient's body to provide diagnostic information.
Blood Banking
The process of collecting, testing, processing, storing, and distributing blood and blood components for transfusions.
National Patient Safety Goals
National Patient Safety Goals are a set of specific aims, established by healthcare organizations, to improve the safety and quality of patient care.
Q4: The Kruskal-Wallis test has less basic assumptions
Q20: Friendly Bank offers you a loan at
Q29: Bayes' Rule allows to calculate the probability
Q33: Replicating in an experiment means that the
Q33: Two variables x<sub>1</sub> and x<sub>2</sub> are said
Q38: Each of the following is true of
Q42: Cash budgets are typically prepared on a(n)
Q47: A firm wants to receive cash earnings.
Q68: Many entrepreneurs are _ diversified with respect
Q78: Christy purchased 100 shares of Good Idea