Use the following to answer question(s) : Computing Monopoly Profit
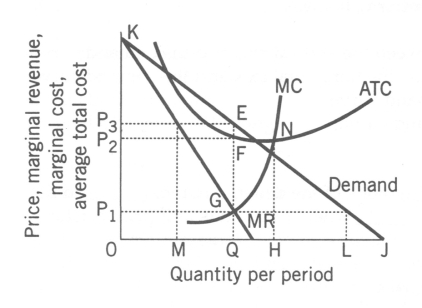
-(Exhibit: Computing Monopoly Profit) When the MR curve crosses the horizontal axis:
Definitions:
Selling Price
Selling price is the amount a buyer pays to purchase a product or service from a seller.
Variable Cost
Costs that change in proportion to the level of goods or services produced, such as materials and labor costs.
Fixed Cost
Costs that do not change with the level of production or sales, such as rent, salaries, and insurance, providing predictability but fixed financial commitments.
Break-Even Point
The financial point at which total revenues exactly equal total costs, resulting in neither profit nor loss.
Q6: The pricing in monopoly prevents some mutually
Q18: (Exhibit: Wage Determination in Perfect Competition)Which of
Q55: A perfectly competitive firm's total revenue:<br>A)curve is
Q65: At 50 units of output, a firm's
Q72: Perfectly competitive factor and output markets are
Q111: Charges that must be paid for the
Q177: Economic profits are guaranteed for:<br>A)a monopoly, but
Q191: Suppose that pasta is produced under conditions
Q203: (Exhibit: Profit Maximizing)The exhibit shows cost curves
Q204: A demand curve that is linear and