Reference: 10127 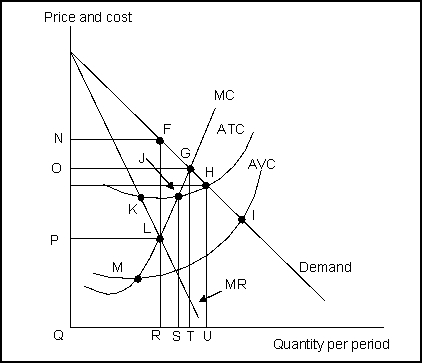
-(Exhibit: Short-Run Monopoly) The output at which marginal cost = price is determined by the intersection at point:
Definitions:
Social Learning
The theory that people can learn new behaviors by observing and imitating others, as well as by receiving rewards and punishments.
Operant Conditioning
A learning process through which the strength of a behavior is modified by reinforcement or punishment.
Latent Learning
Pertains to knowledge acquired without any immediate or visible reinforcement or outcome, becoming apparent only when needed.
Injunctive Norm
A belief about what behaviors are generally approved of or disapproved of in one’s culture.
Q12: (Exhibit: Short-Run Costs)Curve A is the _
Q43: (Exhibit: Demand, Elasticity, and Total Revenue)When price
Q63: In a perfectly competitive market:<br>A)there are barriers
Q85: In the short run, if AVC <
Q133: Imperfectly competitive markets include:<br>A)a category where many
Q157: (Exhibit: Computing Monopoly Profit)At point E, the
Q172: Unlike a perfectly competitive firm, a monopoly
Q183: When the profit-maximizing level of output is
Q233: The supply curve found by summing up
Q257: The firm's supply curve in perfect competition