(Adapted from "Problem Eleven" from Chapter Six of previous editions of the textbook)
Alpha Ltd. is a Canadian-controlled private corporation operating a small land-development business. In June 20x2, the company acquired a license to manufacture pre-fab homes and began operations immediately. Financial information for the 20x2 taxation year is outlined below:
Alpha's profit before income taxes for the year ended November 30, 20x2, was $245,000, as follows:
 The loss on sale of property resulted from two transactions. On October 1, 20x2, Alpha sold all of its shares of Q Ltd., a 100% subsidiary, for $100,000. (The shares were acquired seven years ago for $80,000.) Also, during the year, Alpha sold some of its vehicles for $25,000. The vehicles originally cost $50,000 and had a book value of $48,000 at the time of sale. New vehicles were obtained under a lease arrangement.
The loss on sale of property resulted from two transactions. On October 1, 20x2, Alpha sold all of its shares of Q Ltd., a 100% subsidiary, for $100,000. (The shares were acquired seven years ago for $80,000.) Also, during the year, Alpha sold some of its vehicles for $25,000. The vehicles originally cost $50,000 and had a book value of $48,000 at the time of sale. New vehicles were obtained under a lease arrangement.
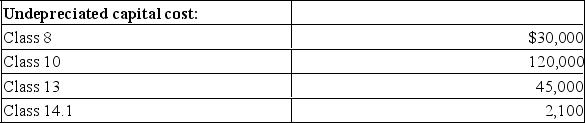
The 20x1 corporate tax return shows the following UCC balances:
 Alpha occupies leased premises under a seven-year lease agreement that began three years ago. At the time, Alpha spent $60,000 to improve the premises. The lease agreement gives Alpha the option to renew the lease for two three-year periods. Alpha began manufacturing pre-fab homes on June 1, 20x2. At that time, it acquired the following:
Alpha occupies leased premises under a seven-year lease agreement that began three years ago. At the time, Alpha spent $60,000 to improve the premises. The lease agreement gives Alpha the option to renew the lease for two three-year periods. Alpha began manufacturing pre-fab homes on June 1, 20x2. At that time, it acquired the following:
 Accounting amortization in 20x2 amounted to $60,000.
Accounting amortization in 20x2 amounted to $60,000.
Alpha normally acquires raw land, which it then develops into building lots for resale to individuals or housing contractors. In 20x2, it sold part of its undeveloped land inventory to another developer for $400,000. The sale realized a profit of $80,000, which is included in the land-development income above. The proceeds consisted of $40,000 in cash, with the balance payable in five annual instalments beginning in 20x3.
Travel and entertainment expense includes the following:
 Legal and accounting expense includes the following:
Legal and accounting expense includes the following:
 Required:
Required:
Calculate Alpha's net income for tax purposes for the 20x2 taxation year. (Assume 20x2 is 2019.)
Definitions:
Mast/o
Refers to the breast or mastoid processes in medical terminology.
Dactyl/o
refers to a word root indicating fingers, toes, or digits.
Cytoplasm
The material or protoplasm within a living cell, excluding the nucleus, containing various organelles where cellular processes occur.
Nuclear Membrane
The double-layered membrane that encloses a cell's nucleus, controlling the passage of materials in and out.
Q1: Which of the following statements regarding debt
Q5: On March 1, 20x1, Notes Inc. purchased
Q8: How many grams of glucose should be
Q8: Green Co. and Blue Co. are equal
Q8: Which of the following solutions has the
Q9: Steven Co. is a public Canadian corporation
Q51: What is an enteric coating?<br>A) It is
Q77: Total physical units to be accounted for
Q79: Which of the following is a balanced
Q113: In the month of April, a department