Scenario 15-1
Vincent operates a scenic tour business in Boston. He has one bus which can fit 50 people per tour and each tour lasts 2 hours. His total cost of operating one tour is fixed at $450. Vincent's cost is not reduced if he runs a tour with a partially full bus. While his cost is the same for all tours, Vincent charges each passenger his/her willingness to pay: adults $18 per trip, children $10 per trip, and senior citizens $12 per trip. At those rates, on a typical day Vincent's demand is: 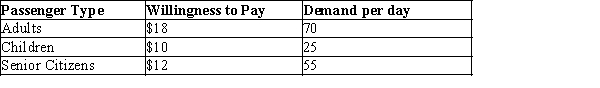 Assume that Vincent's customers are always available for the tour; therefore, he can fill his bus for each tour as long as there is sufficient total demand for the day.
Assume that Vincent's customers are always available for the tour; therefore, he can fill his bus for each tour as long as there is sufficient total demand for the day.
-Refer to Scenario 15-1. One of Vincent's friends tells him he would be more profitable if he charged a single price of $18. Assuming no changes in consumer demand, what would Vincent's profit be if he charged every customer $18?
Definitions:
Plain-Meaning Rule
A principle of legal interpretation that directs courts to interpret statutes according to the ordinary meaning of the language used, absent a clear indication of an alternative intent.
Statutory Interpretation
Statutory interpretation involves the process by which courts determine the meaning and application of legislation.
Rule of Construction
A legal principle used to interpret the meaning and intent of statutes, contracts, or other legal documents.
Statute
A written law passed by a legislative body at the federal, state, or municipal level.
Q3: By comparing the marginal revenue and marginal
Q47: Because nothing can be done about sunk
Q63: When firms in a competitive market have
Q225: The deadweight loss that arises from a
Q228: Land of Many Lakes (LML) sells butter
Q239: Suppose that a professional photographer takes a
Q287: Suppose a competitive market has a horizontal
Q409: Which of these types of costs can
Q431: Refer to Table 14-11. If the firm
Q605: Whenever firms in a perfectly competitive market