In the collision theory of reaction rates, the rate constant for a bimolecular reaction can be written as k = z · p · exp 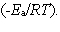 In one sentence each, clearly explain the physical meaning (interpretation) of the following three factors which appear in the above expression:
In one sentence each, clearly explain the physical meaning (interpretation) of the following three factors which appear in the above expression:
A) z
B) p
C) exp 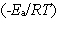
Definitions:
Two-tail Test
A statistical test in which the critical area of a distribution is two-sided and tests whether a sample is either greater than or less than a range of values.
Nominal Data
Data that represents categories with labels or names, where the order of the categories is not meaningful.
Z-test
A statistical test used to determine whether two population means are different when the variances are known and the sample size is large.
Chi-square Test
A statistical test used to determine if there is a significant difference between the observed frequencies and the expected frequencies in one or more categories.
Q10: In molecular orbital theory, combination of two
Q11: In order to write the correct mass-action
Q11: Fill in the blank spaces and write
Q26: Calculate the solubility of silver oxalate, Ag<sub>2</sub>C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>,
Q28: Hydrogen forms metallic (interstitial) hydrides with the
Q37: Bromine is the only nonmetal that is
Q60: Magnesium oxide, MgO, is an important industrial
Q60: . If the compositions of the two
Q95: In the modern periodic table, the order
Q108: Ethane (C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>6</sub>) is much more reactive than