Scenario 9-2
• For a small country called Boxland,the equation of the domestic demand curve for
cardboard is  ,
,
where 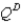 represents the domestic quantity of cardboard demanded,in tons,and
represents the domestic quantity of cardboard demanded,in tons,and 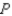 represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
• For Boxland,the equation of the domestic supply curve for cardboard is 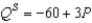 ,
,
where 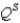 represents the domestic quantity of cardboard supplied,in tons,and
represents the domestic quantity of cardboard supplied,in tons,and 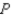 again
again
represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
-Refer to Scenario 9-2.Suppose the world price of cardboard is $45 and international trade is allowed.Then Boxland's consumers demand
Definitions:
Wagner
A reference to theories postulated by Robert A. Rescorla and Allan R. Wagner on conditioning processes, focusing on the associative strength between stimuli and responses.
Unconditioned Response
An automatic, natural response to an unconditioned stimulus that requires no learning.
Pavlov
A Russian physiologist best known for his work in classical conditioning, particularly with the conditioned response of salivation in dogs.
Conditioned Response
A learned reaction to a previously neutral stimulus due to repeated association with an unconditioned stimulus.
Q26: The first digit in a social insurance
Q50: Spain allows trade with the rest of
Q105: Refer to Figure 9-12. With trade, domestic
Q182: Refer to Figure 9-18. If Isoland allows
Q197: The demand for chicken wings is more
Q260: When motorcycles are taxed and sellers of
Q284: One should be especially wary of the
Q393: A tax on a good causes the
Q403: Refer to Figure 8-6. When the government
Q476: Tariffs and quotas are different in the