Figure 34-2.On the left-hand graph,MS represents the supply of money and MD represents the demand for money;on the right-hand graph,AD represents aggregate demand.The usual quantities are measured along the axes of both graphs.
. 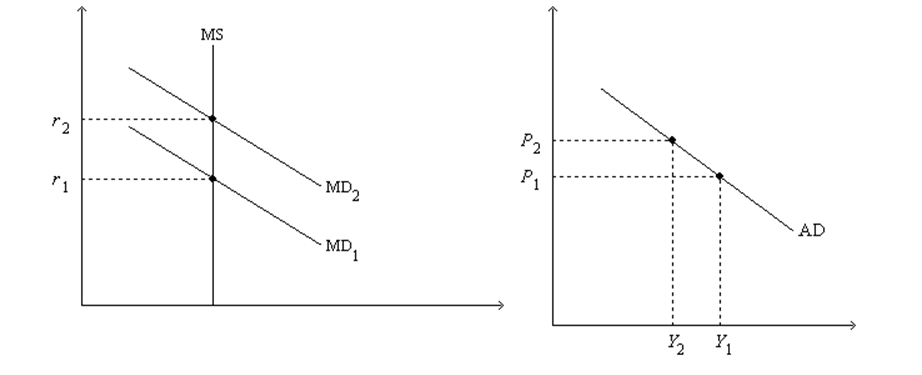
-Refer to Figure 34-2.As we move from one point to another along the money-demand curve MD1,
Definitions:
Risk-neutral
A characteristic of individuals or entities that exhibit indifference between choices with differing levels of risk, focusing solely on expected outcomes.
Expected Utility
A strategy in economics and game theory where individuals choose the option with the highest expected benefit, taking into account all future outcomes.
Risk-neutral
Refers to a mindset or condition where an individual or entity is indifferent to risk when making investment decisions, focusing instead on the potential returns without giving additional weight to the possibility of loss.
Expected Utility
a theory in economics that quantifies how choices are made when outcomes are uncertain, aiming to maximize the expected utility rather than merely the expected monetary value.
Q23: According to the theory of liquidity preference,
Q61: When the government reduces taxes, which of
Q97: When there is an excess demand for
Q257: According to the IGM poll, what percentage
Q360: The term business cycle implies that economic
Q377: The exchange-rate effect is based, in part,
Q408: Refer to Figure 34-6. Suppose the multiplier
Q424: If the spending multiplier is 8, then
Q448: If aggregate demand shifts right, then eventually
Q457: Refer to Figure 33-13. Identify the price