Figure 21-4
In each case, the budget constraint moves from BC-1 to BC-2. 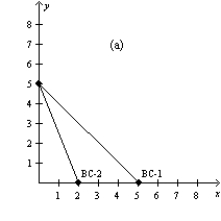
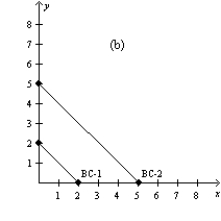
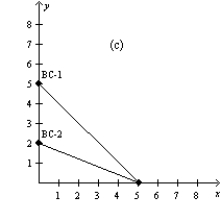
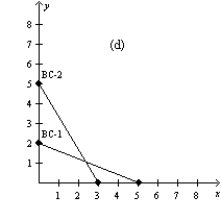
-Refer to Figure 21-4. Which of the graphs in the figure could reflect an increase in income?
Definitions:
Maslow's Need Hierarchy
Maslow's Need Hierarchy is a theory in psychology that categorizes human needs into a five-level pyramid, from basic physiological needs to self-actualization.
Successively Gratify
To provide satisfaction or rewards in a sequential manner, often used as a strategy to maintain motivation and engagement.
Highest Level
The utmost degree or the peak of achievement, performance, or quality in a given context.
McClelland's Need Theory
A motivational theory that identifies three primary needs driving human behavior: Need for Achievement, Need for Power, and Need for Affiliation.
Q24: A disadvantage associated with an Earned Income
Q61: Suppose that you have $100 today and
Q70: The consumer's optimum choice is represented by<br>A)MU<sub>x</sub>/MU<sub>y</sub>
Q126: Which of the following is an advantage
Q155: "The government should choose policies deemed to
Q239: Which of the following is a property
Q297: A government policy aimed at protecting people
Q350: The utilitarian justification for redistributing income is
Q488: If Rita's labor-supply curve is downward-sloping, then
Q547: Because people are more willing to trade