Table 17-5
The information in the table below shows the total demand for premium-channel digital cable TV subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each digital cable TV operator pays a fixed cost of $200,000 (per year) to provide premium digital channels in the market area and that the marginal cost of providing the premium channel service to a household is zero. 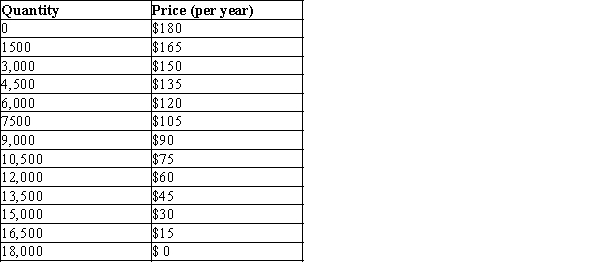
-Refer to Table 17-5. If there is only one digital cable TV company in this market, what price would it charge for a premium digital channel subscription to maximize its profit?
Definitions:
Difference-In-Difference
A statistical technique used to measure the effect of a treatment or intervention by comparing the changes in outcomes over time between a treatment group and a control group.
Free Warranty
A promise or guarantee provided at no extra charge that covers repair or replacement of a product within a specified period.
Type I Errors
The incorrect rejection of a true null hypothesis, also known as a "false positive."
Difference-In-Difference
Difference-in-difference is a statistical technique used in econometrics and quantitative research to measure the effect of a treatment or intervention by comparing the changes in outcomes over time between a group that's exposed to the treatment and a group that's not.
Q90: Refer to Figure 16-3. What is the
Q137: A monopolistically competitive firm is a price-taker.
Q144: Suppose that antitrust laws were successful in
Q218: A cooperative agreement among oligopolists is more
Q221: Refer to Table 17-6. If the market
Q247: Refer to Scenario 18-2. Based on the
Q405: Refer to Scenario 18-2. Labor-market theory assumes
Q406: Refer to Figure 16-13. What is the
Q557: Considering perfect competition, monopolistic competition, and monopoly,
Q641: Oligopoly and monopolistic competition are examples of