Viruses are infectious agents that often cause diseases in plants. Different viruses have different potency levels, and this fact can be used to detect whether a new virus is infecting plants in the field. In a potency comparison experiment, two viruses were placed on a tobacco leaf of 10 randomly selected tobacco plants in a field. The viruses were randomly assigned to one-half of each of the leaves. The table below presents the potency of the viruses, as measured by the number of lesions appearing on the leaf half. 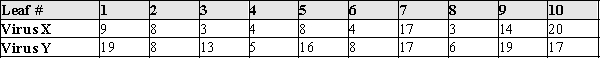 Test the hypothesis that there is no difference in mean number of lesions for Virus X and Virus Y.
Test the hypothesis that there is no difference in mean number of lesions for Virus X and Virus Y.
Definitions:
Inference Forms
Patterns or templates of reasoning that show the logical connection between premises and conclusion.
MP
An abbreviation that could refer to Modus Ponens, a logical form where from premises of the form "If P, then Q" and "P", it's concluded that "Q".
MT
Another term for Modus Tollens, it is the form of logical argument implying the inverse of a conclusion based on the negation of its consequence.
HS
An abbreviation often referring to Hypothetical Syllogism, a logical argument form using two conditional statements to deduce a conclusion.
Q8: A phone bill that totals $ 113
Q8: Suppose a researcher is collecting data to
Q9: The data in the table below are
Q27: An experiment was performed to determine which
Q29: A researcher would like to determine if
Q40: In a few sentences, explain the difference
Q44: Briefly describe how populations and samples differ.
Q47: Artificial bird nests have been used extensively
Q56: The slope of the least squares line
Q81: Provincial sales taxes are remitted to the