Body fat and lean body mass can be estimated in living animals by measuring the total body electrical conductivity (TOBEC). This technique is useful when attempting to determine if "diet drugs" are working on laboratory rats over time--the researchers need not sacrifice the animals to measure the amount of adipose body fat after periods of drug usage. However, the procedure requires that the animal be totally inside the measurement chamber, which is fairly small. Some rats are so big that their tails must be tucked under their bodies before putting them into the measurement chamber. This is causing concern among the researchers, because there is a possibility the tail position might alter the measurements. To see if the TOBEC measurement is altered by the tail position of the rats, an experiment was run on 16 rats ranging in weight from 210 to 505
g.The rats were randomly assigned the order of measurement, with 8 rats measured in the tail-under position first, and 8 rats in the tail-extended position.The data for the body fat measures, and the differences, are presented in the table below. 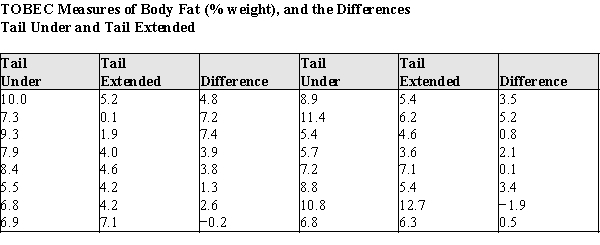 a)Using graphical display(s) of your choice show that the assumptions necessary for the paired t-test are plausible.b)Test the hypothesis that there is no difference between the population mean TOBEC body fat measurements of rats in the tail-under vs.the tail-extended positions.For purposes of the statistics you may assume that these rats are a random sample of laboratory rats.c)Write a short paragraph based on your analysis above, explaining your results for laboratory technicians.Your paragraph should advise them whether or not it is necessary to make sure the tail positions of the rats are the same when replicating the lean mass body measurements during the experiment.
a)Using graphical display(s) of your choice show that the assumptions necessary for the paired t-test are plausible.b)Test the hypothesis that there is no difference between the population mean TOBEC body fat measurements of rats in the tail-under vs.the tail-extended positions.For purposes of the statistics you may assume that these rats are a random sample of laboratory rats.c)Write a short paragraph based on your analysis above, explaining your results for laboratory technicians.Your paragraph should advise them whether or not it is necessary to make sure the tail positions of the rats are the same when replicating the lean mass body measurements during the experiment.
Definitions:
Romanesque Feature
Architectural characteristics typical of the Romanesque style, including rounded arches, solid construction, and extensive use of stone.
Portals
Gateways, either real or symbolic, that connect two distinct areas or realms.
Amiens
A city in northern France, known for its Gothic Amiens Cathedral and its role in World War I and II history.
Rayonnant Style
An architectural style of Gothic architecture, noted for its elaborate decorative elements and emphasis on the play of light, prevalent in the 13th and 14th centuries.
Q4: Data on x = the weight of
Q6: When selecting an appropriate method for data
Q12: A random sample of 120 sixth-graders were
Q14: In the simple linear regression model, the
Q14: The receivables turnover is used to assess
Q29: A subsidiary ledger is used to<br>A) track
Q84: In calculating the present value of an
Q119: RGI Services has just renovated their local
Q122: For the items below, indicate with
Q159: When calculating the present value of an