Additional Application
THE AVERAGE COST OF PRODUCING AIRPLANES
Suppose you want to design and manufacture a new airplane, one with a performance level comparable to the Boeing 737. To get a rough idea of how much it would cost to design the new aircraft and then produce a particular quantity of airplanes, you could use the Airframe Cost Model developed by U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration NASA) . Figure 8.8 shows the average cost of production for up to 100 airplanes. The fixed cost includes the cost of designing the aircraft and the cost of capital used in the production process, including the machine tools used to fabricate the components of the aircraft. Together these fixed costs add up to about $2.45 billion. The variable cost includes the costs of the materials and labor used to produce the components and then assemble the aircraft. The NASA cost model suggests that the average variable cost decreases as the number of airplanes increases because of labor specialization. The average- cost curve in Figure 8.8 is negatively sloped because as the quantity of aircraft increases, the fixed cost is spread over more units and labor specialization pulls down the average variable cost. The average cost decreases from $435 million for a quantity of 10 aircraft, to $257 for 20 aircraft, and so on down to $86 million for 100 aircraft.
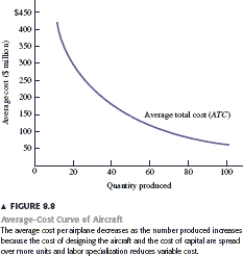 The average-cost curve is negatively sloped, implying that there are no diminishing returns in the production of airplanes. This occurs because the cost model assumes that as output increases, production occurs over a longer period of time. Diminishing returns normally occur if an increase in output requires an increase in the number of workers in a given production facility. In the normal case, each worker becomes less productive because each worker gets a smaller share of the production facility-plant and equipment such as machine tools. But if doubling output means that we operate a given production facility twice as long, diminishing returns wonʹt occur: Each worker still gets the same share of the facility, but simply uses the facility for twice as much time.
The average-cost curve is negatively sloped, implying that there are no diminishing returns in the production of airplanes. This occurs because the cost model assumes that as output increases, production occurs over a longer period of time. Diminishing returns normally occur if an increase in output requires an increase in the number of workers in a given production facility. In the normal case, each worker becomes less productive because each worker gets a smaller share of the production facility-plant and equipment such as machine tools. But if doubling output means that we operate a given production facility twice as long, diminishing returns wonʹt occur: Each worker still gets the same share of the facility, but simply uses the facility for twice as much time.
-Recall the Application on ʺThe Average Cost of Producing Airplanes.ʺ The costs of designing the aircraft and the machine tools used to fabricate the components for the aircraft are:
Definitions:
Trans-Atlantic Trade
Trans-Atlantic Trade refers to the trade that occurred across the Atlantic Ocean, especially notable for the exchange of goods, slaves, and commodities between Africa, Europe, and the Americas from the 16th to the 19th centuries.
Triangular Trade Route
A historical trade system involving the exchange of goods and enslaved people among Europe, Africa, and the Americas.
Major Producer
An entity or individual that significantly contributes to the supply of a particular good or service in the market.
Revenue
The income that a government, organization, or business receives from its activities, often used to fund operations.
Q5: Figure 7.6 shows prices, demands, and cost
Q46: Farmer Brown sells her wheat in a
Q78: A firm doubled all its inputs and
Q85: When a firm is experiencing diminishing returns:<br>A)average
Q111: Suppose that Gigantic Company is increasing in
Q129: Suppose that Figure 7.5 shows a monopolistʹs
Q140: Recall the Application. Does the article suggest
Q144: Suppose that the elasticity of demand for
Q147: Which of the following is NOT a
Q186: If the price elasticity of demand is