Figure 15.3
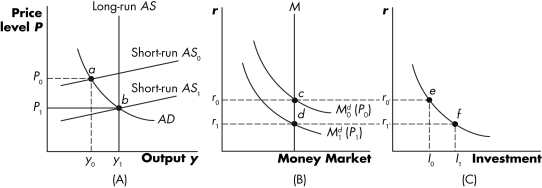
-Explain why money is neutral in the long run.
Definitions:
Absolute Advantage
The capability of an individual, company, or country to produce a good or service at a lower cost per unit than competitors.
Comparative Advantage
The ability of an entity to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than another entity, leading to more efficient trade and production.
Comparative Advantage
The ability of an entity to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than others.
Opportunity Costs
The cost of forgoing the next best alternative when choosing among multiple options, measuring the trade-off involved in any decision.
Q13: The rate at which nations will exchange
Q31: According to this Application, the Fed increased
Q39: Financial monetary assets which often cannot be
Q69: Recall the Application. In response to the
Q78: Refer to Figure 15.2. A decrease in
Q94: An example of a consumption tax is<br>A)
Q105: In _, monetary policy can change the
Q106: If the Fed wished to decrease GDP,
Q114: Purchases of goods and services are included
Q137: By raising the discount rate, the Federal