Figure 34-7
(a) The Money Market
(b) The Aggregate Demand Curve 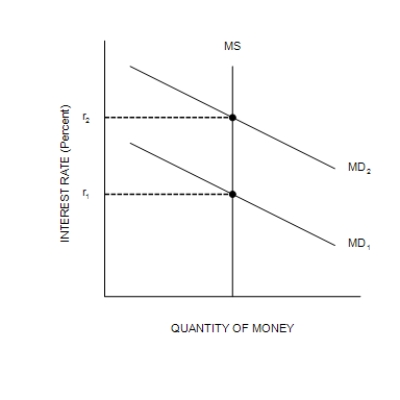
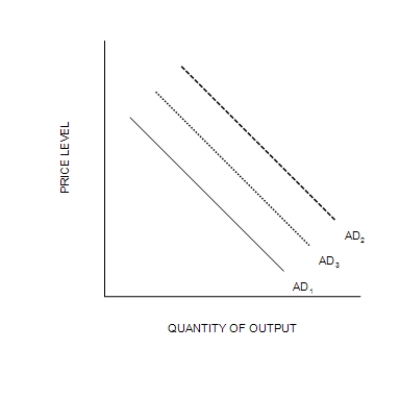
-Refer to Figure 34-7. Suppose the multiplier is 5 and the government increases its purchases by $15 billion. Also, suppose the AD curve would shift from AD1 to AD2 if there were no crowding out; the AD curve actually shifts from AD1 to AD3 with crowding out. Also, suppose the horizontal distance between the curves AD1 and AD3 is $55 billion. The extent of crowding out, for any particular level of the price level, is
Definitions:
Null Hypothesis
The hypothesis that there is no significant difference or effect, serving as the default assumption to be tested against the alternative hypothesis.
Population Proportions
The ratio of members in a statistical population that have a particular attribute or characteristic.
Type I Error
A statistical error that occurs when a true null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected.
Type II Error
The error that occurs when a statistical test fails to reject a false null hypothesis, incorrectly concluding that there is no effect or difference when there is.
Q1: An improved functioning of the labor markets
Q5: In an open economy, the demand for
Q14: A rightward shift of the short-run aggregate-supply
Q29: Explain the logic according to liquidity preference
Q34: The multiplier effect states that there are
Q93: When output rises, unemployment falls.
Q96: Which of the following reduce the incentive
Q106: The theory of _ states that the
Q195: Other things the same, which of the
Q223: A low sacrifice ratio would make a