Figure 15-12
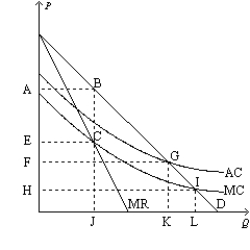
-Refer to Figure 15-12. If a regulator requires this firm to charge a socially optimal price, how much deadweight loss results?
Definitions:
Annual Interest Payments
These are payments made to lenders or bondholders for the use of borrowed money, typically calculated annually based on the interest rate and principal amount.
Yield To Call (YTC)
The rate of interest earned on a bond if it is called. If current interest rates are well below an outstanding callable bond��’s coupon rate, the YTC may be a more relevant estimate of expected return than the yield to maturity, since the bond is likely to be called.
Yield To Maturity (YTM)
The total return anticipated on a bond if the bond is held until its maturity date, taking into account both interest payments and the difference between the bond's current market price and its face value.
Annual Coupon Rate
A bond's yearly interest payment to its holders, expressed as a percentage of the bond's face value.
Q3: Refer to Figure 16-10. Does this monopolistically
Q28: The equilibrium quantity in markets characterized by
Q49: When it produces and sells 90 units
Q50: The Clayton Act of 1914 allowed a
Q55: A competitive firm sells 100 units of
Q95: Adam Smith describes a visit to a
Q130: Refer to Figure 14-7. Suppose a firm
Q150: For a profit-maximizing firm in a monopolistically
Q187: A firm is currently producing 100 units
Q227: Refer to Figure 14-1. The firm should