Table 3-11
Assume that Bahamas and Denmark can switch between producing coolers and producing radios at a constant rate.
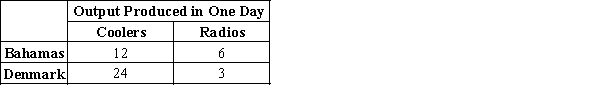
-Refer to Table 3-11. Assume that Bahamas and Denmark each has 4 days available for production. Originally, each country divided its time equally between the production of coolers and radios. Now, each country spends all its time producing the good in which it has a comparative advantage. As a result, the total output of radios increased by
Definitions:
Step-Wise Variable Cost
A cost that remains fixed within a certain level of activity but will jump to a higher amount at a certain point due to increased activity.
Variable Costs
Costs that change in proportion to the level of activity or production volume.
Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
An accounting method used to determine the effects of changes in costs and volume on a company's profits.
Relevant Range
The range of activity within which the assumptions about fixed and variable cost behavior are valid.
Q38: If a country has the comparative advantage
Q50: Which of the following statements exemplifies a
Q58: A decrease in demand shifts the demand
Q132: Inflation measures the increase in the quantity
Q134: Suppose a war in the Middle East
Q167: A circular-flow diagram is a visual model
Q176: A decrease in the price of peanut
Q192: A marginal change is a small incremental
Q198: Refer to Figure 2-3. Suppose this economy
Q255: When two variables move in the same