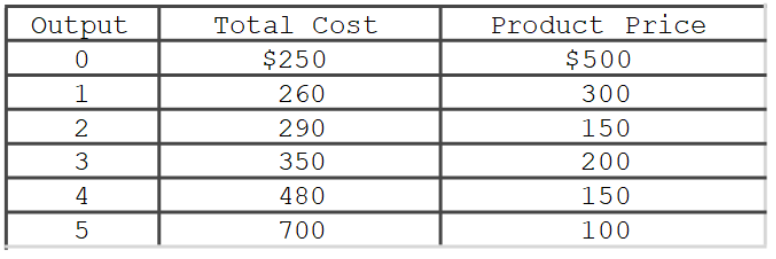
If the profit-maximizing pure monopolist whose information is in the accompanying table is able to price discriminate, charging each customer the price associated with each given level of output, how much profit will the firm earn?
Definitions:
Opportunity Cost
The cost of forgoing the next best alternative when making a decision, reflecting the potential benefits one misses out on when choosing one option over another.
Bowed Outward
Describes a curve on a graph, typically a production possibility frontier, indicating increasing opportunity costs when shifting resources between two goods.
Opportunity Cost
The cost of choosing one option over another, typically the best alternative forgone as a result of making a decision.
Efficient
Efficiency refers to the optimal production and distribution of resources in a way that best meets the needs and desires of consumers.
Q6: When a competitive firm sees the price
Q59: Firms must consider the possible reaction of
Q93: A price-discriminating monopolist will follow a system
Q97: If the several oligopolistic firms that compose
Q105: In the standard model of pure competition,
Q112: Which is a major criticism of a
Q113: In the long run, assuming that market
Q114: The primary force encouraging the entry of
Q114: The MR = MC rule<br>A)applies only to
Q158: In which market model is there mutual