Canadian Accounting classifies accounts receivable as "current", "late", and "not collectible". Industry figures show that 60% of A/R are current, 30% are late, and 10% are uncollectible. A law firm in Markham Ontario has 500 accounts receivable: 320 are current, 120 are late and 60 are not collectible. Are these numbers in agreement with the industry distribution? 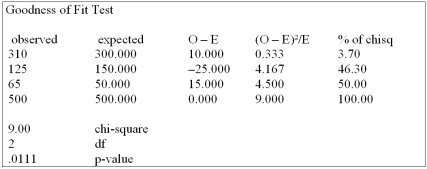
Definitions:
Accrual Entry
An accounting method that records revenues and expenses when they are incurred, regardless of when cash is exchanged.
Accounting Accruals
Accounting method where revenue and expenses are recorded when they are earned or incurred, not necessarily when cash is received or paid.
Unpaid Payroll
The total sum of all wages, salaries, bonuses, and deductions owed to employees that have not yet been paid.
Depreciation
The accounting process of allocating the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life, reflecting decrease in value over time.
Q1: Of 150 adults who tried a new
Q15: Which of the following is NOT a
Q22: A linear trend equation is used to
Q31: Hypotheses concerning individual regression coefficients are tested
Q49: Exercise: Are you familiar with the word,
Q78: Any definition by example of the word
Q84: Listed below is the net sales in
Q89: Which of the following is a characteristic
Q96: Determine whether the following passage contains an
Q218: Which of the following is a matter