Determine whether the linear transformation T is one-to-one and whether it maps as specified.
-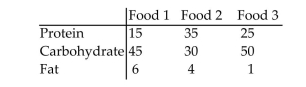
Betty would like to prepare a meal using some combination of these three foods. She would like the meal to contain of protein, of carbohydrate, and of fat. How many units of each food should she use so that the meal will contain the desired amounts of protein, carbohydrate, and fat? Round to 3 decimal places.
Definitions:
Specific Goals
Clear, defined, and measurable objectives that one aims to achieve within a certain timeframe.
Specified Period
A fixed or clearly defined duration of time.
Dietary Assessment Method
Techniques or tools used to evaluate the nutritional value of a person's diet, often through the collection and analysis of dietary intake data.
Usual Intake Form
A dietary assessment tool used to record an individual's typical food and beverage consumption over a specific period.
Q1: In <span class="ql-formula" data-value="R ^
Q3: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\mathbf { y } =
Q17: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\begin{array} { l } 7
Q17: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\left[ \begin{array} { r r
Q18: The frequency table below shows the
Q33: Emily Corp.owned shares in Carr Ltd.On December
Q41: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="B = \left[ \begin{array} {
Q56: For what values of h are
Q263: If, during an accounting period, an expense
Q329: When expenses are presented by function in