The neoclassical growth model predicts that for identical savings rates and population growth rates, countries should converge to the per capita income level. This is referred to as the convergence hypothesis. One way to test for the presence of convergence is to compare the growth rates over time to the initial starting level, i.e., to run the regression , where is the average annual growth rate of GDP per worker for the 1960-1990 sample period, and is GDP per worker relative to the United States in 1960. Under the null hypothesis of no convergence, , implying ("beta") convergence. Using a standard regression package, you get the following output: Dependent Variable: G6090
Method: Least Squares
Date: 07/11/06 Time: 05:46
Sample: 1104
Included observations: 104
White Heteroskedasticity-Consistent Standard Errors & Covariance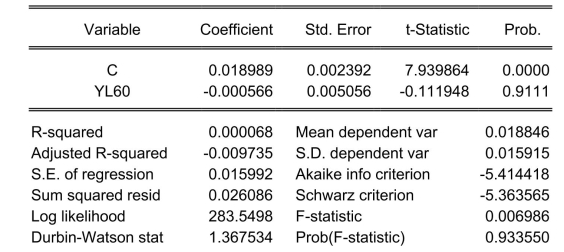
You are delighted to see that this program has already calculated p-values for you.
However, a peer of yours points out that the correct p-value should be 0.4562.
Who is right?
Definitions:
Empathy
The capacity to understand or feel what another person is experiencing from within their frame of reference.
Prosocial Behavior
Voluntary actions intended to benefit or help others, such as sharing, comforting, or rescuing.
Sympathy
Feelings of pity or sorrow for someone else's misfortune.
Temperament
Refers to the innate aspects of an individual's personality, such as their tendency towards certain moods or behaviors.
Q2: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\mathrm { E } \left(
Q4: Discuss the properties of the OLS estimator
Q5: The neoclassical growth model predicts that for
Q11: Besides maximum likelihood estimation of the logit
Q23: Let there be q
Q24: When the sample size n
Q29: The slope estimator, <span class="ql-formula"
Q36: Describe the process for making a tree
Q38: The following data show the number
Q59: Determine whether the given value is a