Parallel lines are cut by the transversal shown. Determine the measures of the requested angles.
-In the figure, and . Determine the measures of angles , and 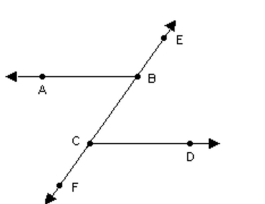
Definitions:
Insignificant Variables
Variables in a statistical model that do not have a significant impact on the model's ability to predict or describe the outcome.
Variables
Any characteristic, number, or quantity that can be measured or quantified, which changes or varies across different situations or observations.
Crime Rates
Quantitative measures that reflect the number of crimes committed per unit of population or area in a specific time frame.
Pearson Correlation Coefficients
A measure of the linear correlation between two variables X and Y, giving a value between -1 and 1 inclusive, where 1 is total positive linear correlation, 0 is no linear correlation, and -1 is total negative linear correlation.
Q6: A writer for an art magazine randomly
Q15: The payroll amounts for 26 major-league baseball
Q46: The graph below is an ogive of
Q48: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3046/.jpg" alt=" A) Parallelogram B)
Q82: A long-distance runner runs 2 miles south
Q88: [(11 ∙ 4) + 4] (mod 8)<br>A)
Q111: 3 is divisible by 6.
Q141: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3046/.jpg" alt=" A)
Q170: Hye-Ran, who is 1.60 m tall, wishes
Q178: The diameter of a bolt.<br>A) decimeters<br>B) meters<br>C)