Apply the expected value approach to decision making.
-A land owner is considering a community development project in the southeastern U.S.
He is faced with two alternatives: (1) build detached homes in a planned retirement
Community or (2) build a smaller townhouse / condominium complex. Mortgage interest
Rates will affect his outcomes and the payoff (in $ millions) table is shown below. If the
Probabilities for future mortgage interest rates going up, staying about the same, and
Going down are .35, .50 and .15, respectively, the best decision according to the expected
Value approach is to 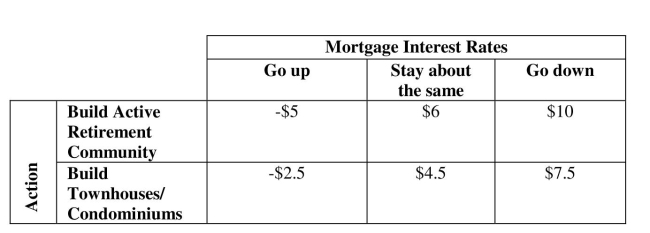
Definitions:
Even Dollar Increments
A pricing strategy where goods or services are priced in whole dollar amounts rather than including cents.
Complete Stranger
A person whom one does not know or with whom one is not familiar.
Expected Loss
The predicted amount of loss a business might suffer due to risks, calculated as the sum of all possible losses multiplied by their respective probabilities.
Weak Axiom
A principle used in consumer choice theory that stipulates if a consumer chooses bundle A over bundle B when both are affordable, then the consumer should not choose B over A when prices change, holding income constant.
Q4: Determine which type of drink had the
Q6: What affects flat panel LCD TV
Q15: A large national retailer of electronics
Q20: Are the assumptions and conditions for constructing
Q21: A small flower shop takes orders by
Q71: A medical doctor is involved in a
Q101: To calculate expected profit under certainty, you
Q114: Referring to Scenario 18-4, suppose the
Q142: Referring to Scenario 18-4, what is
Q272: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="| x + 1 |