SCENARIO 16-13
Given below is the monthly time series data for U.S. retail sales of building materials over a
specific year. Month 123456789101112 Retail Sales 6,5946,6108,1749,51310,59510,4159,9499,8109,6379,7329,2149,201 The results of the linear trend, quadratic trend, exponential trend, first-order autoregressive,
second-order autoregressive and third-order autoregressive model are presented below in which
the coded month for the 1st month is 0: Linear trend model:
Intercept Coded Month Coefficients 7950.7564212.6503 Standard Error 617.634295.1145 t Stat 12.87292.2357 P-value 0.00000.0494
Quadratic trend model:
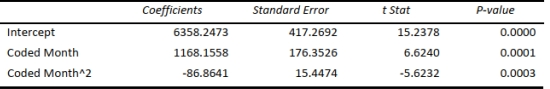
Exponential trend model:
Intercept Coded Month Coefficients 3.89120.0116 Standard Error 0.03150.0049 t Stat 123.36742.3957 P-value 0.00000.0376
First-order autoregressive:
Intercept YLag1 Coefficients 3132.09510.6823 Standard Error 1287.28990.1398t Stat 2.43314.8812 P-value 0.03780.0009
-Referring to Scenario 16-13, what is the exponentially smoothed forecast for the 13th month
using a smoothing coefficient of W = 0.5 if the exponentially smooth value for the 10th and 11th month are 9,746.3672 and 9,480.1836, respectively?
Distinguish between different AI approaches such as machine learning, neural networks, and natural language processing.
Understand how AI can analyze massive datasets to recognize patterns and make recommendations (data mining).
Recognize how technology enables creativity and the sharing of information (cognitive surplus).
Identify methods and tools for enhancing reality and human experience through technology (augmented reality, affective computing).
Definitions:
Direct Write-off Method
An accounting method where uncollectible accounts receivable are directly written off against income at the time they are deemed uncollectible.
Uncollectible Receivables
Amounts owed to a company that it does not expect to collect and thus considers a loss.
Journalize
The process of recording transactions in an accounting journal, noting the debit and credit aspects of each transaction.
Percent of Sales Method
A financial analysis technique used to forecast future expenses or account balances as a percentage of sales revenue.
