SCENARIO 15-1 A certain type of rare gem serves as a status symbol for many of its owners.In theory, for low prices, the demand increases, and it decreases as the price of the gem increases.However, experts hypothesize that when the gem is valued at very high prices, the demand increases with price due to the status owners believe they gain in obtaining the gem.Thus, the model proposed to best explain the demand for the gem by its price is the quadratic model: 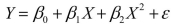 where Y = demand (in thousands) and X = retail price per carat. This model was fit to data collected for a sample of 12 rare gems of this type.A portion of the computer analysis obtained from Microsoft Excel is shown below: SUMMARY OUTPUT
where Y = demand (in thousands) and X = retail price per carat. This model was fit to data collected for a sample of 12 rare gems of this type.A portion of the computer analysis obtained from Microsoft Excel is shown below: SUMMARY OUTPUT 


-Referring to Scenario 15-1, what is the value of the test statistic for testing whether there is an upward curvature in the response curve relating the demand (Y) and the price (X) ?
Definitions:
ERV
Expired Reserve Volume; the additional amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled after the completion of a normal, quiet expiration.
AFB
Acid-fast bacillus, a type of bacteria that is resistant to decolorization by acids during staining procedures; commonly used to refer to tuberculosis-causing bacteria.
MDR TB
Multi-Drug Resistant Tuberculosis, a form of TB that is resistant to at least isoniazid and rifampicin, the two most powerful tuberculosis drugs.
Chronic Pulmonary Disease
A group of lung diseases that block airflow and make it difficult to breathe; commonly includes conditions like chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
Q34: Referring to Scenario 15-7-A, the model
Q47: Referring to Scenario 14-4, one individual in
Q51: You need to decide whether you should
Q63: Using the best-subsets approach to model
Q143: Referring to Scenario 15-5, what is the
Q162: Referring to Scenario 14-13, the effect of
Q186: Referring to Scenario 16-15-A, what is the
Q231: Referring to Scenario 16-3, if this series
Q253: In real-world business analytics, filtering is typically
Q315: Referring to Scenario 17-9, the 0 to