SCENARIO 14-16
What are the factors that determine the acceleration time (in sec.) from 0 to 60 miles per hour of a
car? Data on the following variables for 30 different vehicle models were collected: (Accel Time): Acceleration time in sec.
(Engine Size): c.c.
(Sedan): 1 if the vehicle model is a sedan and 0 otherwise
The regression results using acceleration time as the dependent variable and the remaining variables as the independent variables are presented below.
ANOVA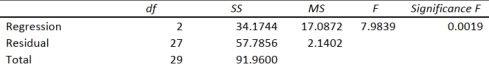
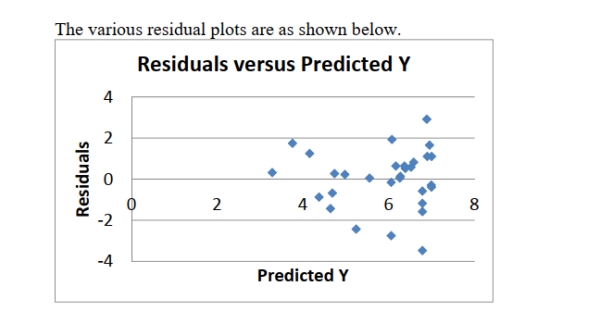
-Referring to Scenario 14-16, the error appears to be left-skewed.
Definitions:
Vasodilation
The dilation of blood vessels, which decreases blood pressure.
Motivation
Motivation is the psychological driving force that initiates and guides behavior, often driven by the desire to fulfill a need or achieve a goal.
Internal Cues
Psychological or physiological signals from within the body that can trigger certain responses, such as hunger cues indicating the need to eat.
Glucose
A simple sugar and a key energy source for the body, critically involved in cellular respiration and the production of ATP.
Q12: Referring to Scenario 13-3, suppose the director
Q45: Referring to Scenario 13-4, the total sum
Q50: Referring to Scenario 13-3, suppose the director
Q91: Referring to Scenario 15-6, the model
Q100: Referring to Scenario 14-19, what is the
Q172: Referring to Scenario 12-10, what is the
Q173: Referring to Scenario 13-14-A, the p-value of
Q222: Referring to Scenario 13-14-A, the conclusion on
Q272: Referring to Scenario 14-7, the department
Q367: Referring to Scenario 14-14, the fitted model