SCENARIO 14-16
What are the factors that determine the acceleration time (in sec.) from 0 to 60 miles per hour of a
car? Data on the following variables for 30 different vehicle models were collected: (Accel Time): Acceleration time in sec.
(Engine Size): c.c.
(Sedan): 1 if the vehicle model is a sedan and 0 otherwise
The regression results using acceleration time as the dependent variable and the remaining variables as the independent variables are presented below.
ANOVA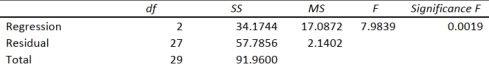
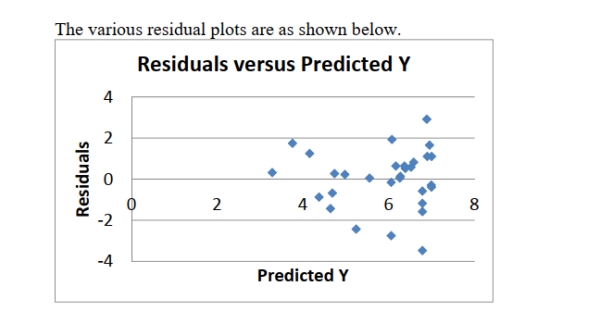
-Referring to Scenario 14-16, the error appears to be left-skewed.
Definitions:
Potential Profit
The projected or anticipated profit from a business activity or investment, considering current or expected conditions.
Transfer Price
Transfer price refers to the price at which goods and services are sold between departments or subsidiaries within the same company.
Selling Division
The division or section of a company responsible for sales activities and interfacing with customers to sell products or services.
Buying Division
A department or segment within a company responsible for purchasing goods, materials, or services.
Q21: Referring to Scenario 13-4, the managers of
Q23: Referring to Scenario 13-9, the 90% confidence
Q59: Referring to Scenario 15-7-A, the model
Q73: Referring to Scenario 13-11, what is the
Q82: Referring to Scenario 13-11, which of the
Q109: Referring to Scenario 15-5, what is the
Q155: Referring to Scenario 14-10, the 99% confidence
Q185: Referring to Scenario 14-13, the fitted
Q187: Referring to Scenario 12-1, if the
Q249: Referring to Scenario 14-19, what is the