Perform the required hypothesis test by using a Mann-Whitney test. Use a normal approximation for M. Find the meanand standard deviation of M, the value of M and of the test statistic, the critical value(s), and state your conclusion.
-A person who commutes to work is choosing between two different routes. He tries the first route 11 times and the second route 12 times and records the time of each trip. The results (in minutes)are shown below. Use a significance level of 0.01 to test whether the mean time for route 1 differs from the mean time for route 2. 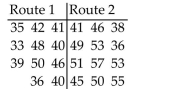
Definitions:
Density Function
A mathematical function that describes the distribution of a continuous random variable, indicating the probability of the variable falling within a particular range.
Exponentially Distributed
Pertaining to a statistical distribution characterized by a constant rate of decay or growth over time.
Random Variable
A variable whose outcomes are determined by the occurrences of a random event.
Exponential Random Variable
A type of random variable that describes the time between events in a Poisson process, representing occurrences that happen at a constant rate.
Q19: Based on a random sample of
Q24: Suppose that past history shows that 60%
Q26: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\begin{array}{c|ccccc}\mathrm{x} & 0 & 3
Q27: To test the effectiveness of a business
Q50: A company that manufactures designer jeans is
Q54: Referring to Scenario 20-1, if the probability
Q56: Suppose that you wish to perform
Q65: The director of admissions at a state
Q96: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\begin{array}{l} \text { Use the
Q105: Referring to Scenario 18-2, what is the