There are four independent variables, , and , that might be useful in predicting a response . A total of observations is available, and it is decided to employ stepwise regression to help in selecting the independent variables that appear to useful. The computer fits all possible one-variable models of the form . The information in the table is provided from the computer printout.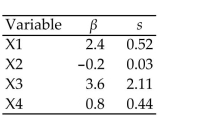
Which independent variable is declared the best one-variable predictor of ?
Definitions:
Variable
A characteristic, number, or quantity that can change or vary, often used in research to measure and analyze differences or effects.
Experimental Group
A group in a scientific study that receives the treatment or intervention being tested, allowing researchers to measure the effect of the treatment.
Control Group
In experimental research, the group of subjects not exposed to the treatment, used as a benchmark to measure the effect of the treatment group.
Randomization Technique
A method used in experiments to randomly assign subjects to different groups to reduce bias and ensure the groups are comparable.
Q14: A consumer protection organization claims that
Q29: A local consumer reporter wants to compare
Q30: Indicate where the event paid income taxes
Q31: Gold Clothing Store had a balance
Q37: Locate the values of <span
Q42: Use the appropriate table to find
Q47: Calculating financial ratios is a financial reporting
Q88: A rental company offers 12 choices of
Q91: By examining the statement of cash flows,
Q123: The following information pertains to Soho