In a comprehensive road test for new car models, one variable measured is the time it
takes the car to accelerate from 0 to 60 miles per hour. To model acceleration time, a
regression analysis is conducted on a random sample of 129 new cars. TIME60: = Elapsed time (in seconds) from to
MAX: Maximum speed attained (miles per hour)
The simple linear model was fit to the data. Computer printouts for the analysis are given below:
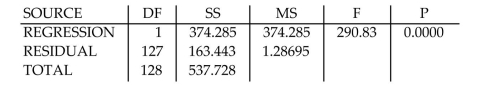
CASES INCLUDED 129 MISSING CASES 0
Definitions:
Tax Expense
Tax Expense is the total amount of taxes owed by an individual or corporation to the federal, state, and local government, reflecting in the financial statements of the period in which the tax is accrued.
Premium Amortization
The systematic reduction of a premium paid above the par value of a bond, allocated over the bond's life until maturity.
Bond Amortization Schedule
A schedule that details the reduction of a bond's principal amount over time, often including payments of both principal and interest.
Unamortized Premium
The portion of a bond premium that has not yet been amortized or gradually written off over time.
Q10: All major financing and investing activities affect
Q10: The contingency table below shows the
Q13: A scientist is hoping to compare
Q30: Vertical analysis is also called<br>A)common size analysis.<br>B)horizontal
Q32: A multinomial experiment with k =
Q41: Measures of a company's liquidity are concerned
Q49: During one recent year, U.S. consumers redeemed
Q79: 307 diamonds were sampled and randomly
Q121: A sociologist recently conducted a survey
Q130: During the year, Income Tax Expense amounted