Homelessness is a problem in many large U.S. cities. To better understand the problem, a
multiple regression was used to model the rate of homelessness based on several
explanatory variables. The following data were collected for 50 large U.S. cities. The
regression results appear below. Homeless number of homeless people per 10,000 in a city Poverty percent of residents with income under the poverty line Unemployment percent of residents unemployed Temperature average yearly temperature (in degrees .)
Dependent variable is Homeless
squared squared (adjusted)
with degrees of freedom
a. Using a 5% level of significance, which variables are associated with the number of
homeless in a city?
b. Explain the meaning of the coefficient of temperature in the context of this problem.
c. Explain the meaning of the coefficient of rent control in the context of this problem.
d. Do the results suggest that having rent control laws in a city causes higher levels of
homelessness? Explain.
e. If we created a new model by adding several more explanatory variables, which statistic
should be used to compare them
f. Using the plots below, check the regression conditions. 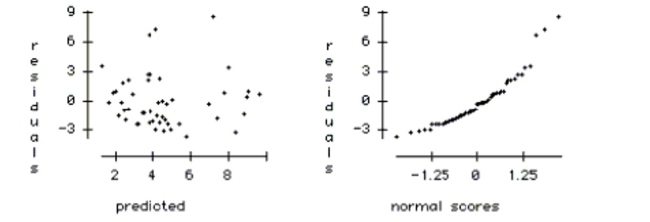
Definitions:
Mutually Exclusive Projects
Investment projects where the acceptance of one project prevents the acceptance of another due to resource constraints or other factors.
Net Present Values
The gap between the present value of cash entering and the present value of cash exiting over a certain period, used within capital budgeting to gauge the financial viability of an investment.
Payback Period
The duration it takes for an investment to generate enough cash flow to recover its initial cost.
Average Accounting Returns
A financial ratio that measures a firm's average profitability relative to its investment, typically calculated as net income divided by average book value of investment.
Q17: Last weekend police ticketed 18 men whose
Q19: It takes a while for new
Q55: An ice cream stand reports that 12%
Q81: a. Sketch a histogram of these data<br>b.
Q347: We want to know the mean winning
Q499: Packing Line A packing company investigates hiring
Q599: Which is important in designing a good
Q628: Email At CPU every student gets a
Q642: Which of the following statements is NOT
Q713: Put to Work Some students have to