The bigger the stop sign, the more expensive it is. Here is a graph of the height of a sign in inches versus its cost in dollars.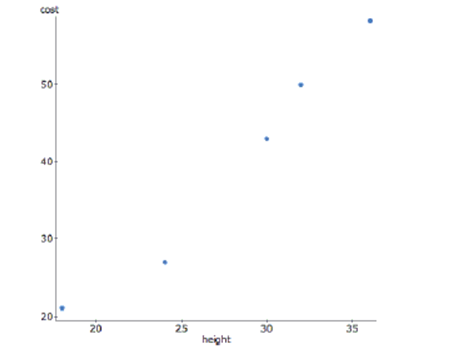
To achieve linearity, the data was transformed using a square root function of cost. Here are the results and a residual plot.
Dependent Variable:
(correlation coefficient)
s: 0.2141
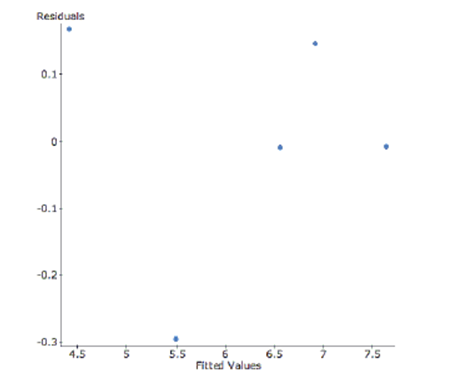
-Interpret R-sq in the context of this problem.
Definitions:
Herfindahl Index
A measure of market concentration and competition, calculated as the sum of the squares of the market shares of all firms within an industry.
Clayton Act
A U.S. antitrust law enacted in 1914 aimed at promoting fair competition and preventing monopolies.
Herfindahl Index
A measure of the size of firms in relation to the industry and an indicator of the amount of competition among them.
Horizontal Merger
A merger between firms that are in the same industry, often aimed at reducing competition and achieving economies of scale.
Q1: Which type of plot would be least
Q5: Describe the kind of bias that might
Q19: It takes a while for new
Q96: Identify what is wrong with each
Q105: If the diameter is increased from 4
Q108: Listed at the right are the
Q397: A survey of local car dealers revealed
Q446: Describe the kind of bias that might
Q514: Graduation tests Many states mandate tests that
Q639: The correlation between a family's weekly income