Use the following information to answer the question. Math self-efficacy can be defined as one's belief in his or her own
ability to perform mathematical tasks. A college math professor wishes to find out if her female students' math self-efficacy
matches reality. To do this she gives a math quiz to the female students then asks them to rate their level of confidence in
how well they did on the quiz. She plans to test whether those who had little confidence that they did well on the quiz
actually performed worse than those who had a high level of confidence that they did well on the quiz. Shown below is the
approximate sampling distribution of the difference in mean quiz scores. The table below shows the summary statistics for
the two groups. Assume that all conditions for a randomization test have been satisfied. 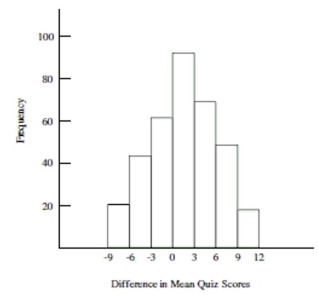
-Carry out the randomization test. What is the professor's conclusion? Are differences in mean quiz scores due to chance?
Definitions:
Market Price
The price for an asset or service in the market at the present time.
Interest Rate Risk
The risk that changes in interest rates will negatively affect the value of an investment, especially those with fixed interest rates.
Coupon
The interest rate stated on a bond when it's issued, which represents the annual interest payment made to bondholders.
Payable Semiannually
This term indicates that a payment, often in the context of bond interest or dividends, is made twice a year.
Q5: The graph below displays the number of
Q11: What was the most common response for
Q19: Which of the following is not true
Q23: Which workout recovery drink is better: water,
Q23: A bridge piling has a cross-sectional
Q35: A horticulturist conducted an experiment on
Q35: Choose the statement that is not true
Q36: What is the name and value
Q46: Which group is more likely to spend
Q50: A group of adults was given a