On a frictionless horizontal surface, a 1.50-kg mass traveling at 3.50 m/s suddenly collides
with and sticks to a 3.00-kg mass that is initially at rest, as shown in the figure. This
system then runs into an ideal spring of force constant (spring constant) 50.0 N/cm.
(a) What will be the maximum compression distance of the spring?
(b) How much mechanical energy is lost during this process? During which parts of the
process (the collision and compression of the spring) is this energy lost? 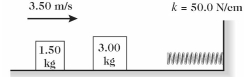
Definitions:
Reconciliation
The process of ensuring that two sets of records (usually the balances of two accounts) are in agreement. It is a key accounting process.
Segment Profit Margin Analysis
The process of evaluating the profitability of different segments or divisions within a company.
Segment Liabilities
The liabilities related to a single reportable segment of a business, as opposed to the entire organization.
Total Segment Expenses
The combined costs incurred by a specific segment of a business within a given period, including both direct and allocated expenses.
Q3: Identical forces act for the same length
Q5: The figure shows scale drawings of four
Q6: The cosmic background radiation corresponds to a
Q16: A solid uniform sphere is rolling
Q27: If a spring-operated gun can shoot a
Q27: When the pressure applied to an
Q64: An object hits a wall and bounces
Q111: A horizontal 52-N force is needed to
Q113: Three objects are moving along a
Q131: The figure shows two boxes, with