As shown in the figure, a 1.45-kg block is held in place against the spring by a 21-N horizontal external force. The external force is removed, and the block is projected with a velocity =1.2 m/s as it separates from the spring. The block descends a ramp and has a velocity at the bottom. The track is frictionless between points A and B . The block enters a rough section at B , extending to E. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the rough surface is 0.29 . The velocity of the block is at C. The block moves on to D, where it stops. How much work is done by friction between points B and C ?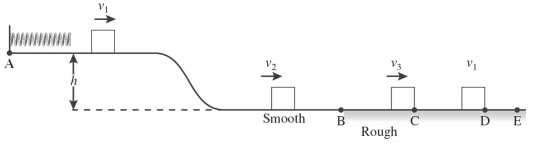
Definitions:
Producer Surplus
The difference between what producers are willing to accept for a good versus what they actually receive, evidencing economic benefit.
Costume Jewelry
Jewelry made from inexpensive materials and imitation gems, designed to provide an attractive appearance at a lower cost than jewelry made from precious metals and stones.
Consumer Surplus
The difference between what consumers are willing to pay for a good or service versus what they actually pay.
Equilibrium Price
The price at which the quantity of a good demanded by consumers equals the quantity supplied by producers.
Q17: Which of the following particles (or groups
Q24: A person carries a 2.00-N pebble
Q29: In the nuclear reaction <span
Q42: How large a net force is required
Q49: A hypothetical planet has a mass of
Q53: The kinetic friction force that a horizontal
Q55: A 1200-kg car is pulling a 500-kg
Q68: Isotope A has a decay constant
Q72: A puck with a mass
Q144: The rotating systems shown in the