A radiometer has two square vanes by , attached to a light horizontal cross arm, and pivoted about a vertical axis through the center, as shown in the figure. The center of each vane is from the axis. One vane is silvered and it reflects all radiant energy incident upon it. The other vane is blackened and it absorbs all incident radiant energy. Radiant energy, having an intensity of , is incident normally upon the vanes. What is the radiation pressure on the blackened vane? 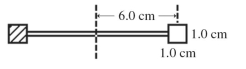
Definitions:
Qualitative Designs
Research methodologies that focus on gathering non-numerical data to understand concepts, perceptions, or experiences.
Quantitative Approaches
Research methods focusing on the collection and analysis of numerical data to understand patterns, relationships, and causality.
Rich Descriptions
Detailed, nuanced accounts of phenomena, typically in qualitative research, that aim to capture the complexity and context of the subject matter.
Experimental Control
The practice of eliminating or managing variables that can affect the outcome of an experiment, except for the variable being studied.
Q50: Microbial products can be improved by all
Q57: All of the following are reasons for
Q65: When unequal resistors are connected in parallel
Q105: The lattice spacing of the principal
Q131: The eyepiece of a compound microscope has
Q132: A crystal is irradiated with x-rays
Q134: The objective lens of a microscope has
Q151: Suppose you place an object in front
Q261: The figure shows a graph of the
Q522: An object is moving with constant non-zero