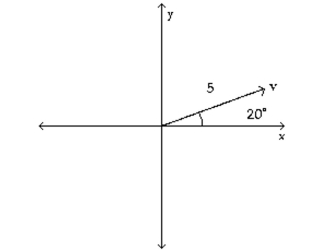
Write the vector in the form <a, b>. If necessary, round values to the nearest hundredth.
-
Definitions:
Continuous Random Variables
Variables that can take an infinite number of values within a given range.
Infinite
A term describing a quantity without bounds or end, often used in mathematics and physics.
Continuous Probability Distributions
Probability distributions in which the data can take infinitely many values within a given range.
Poisson Probability Distribution
A discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time or space, assuming these events occur with a known constant mean rate and independently of the time since the last event.
Q5: After obtaining a regression line
Q10: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7900/.jpg" alt=" " class="answers-bank-image d-block" rel="preload"
Q20: Managers rate employees according to job
Q24: A manager records the production output
Q30: The following table shows the mileage
Q31: Given that the rank correlation coefficient, rs,
Q78: A sample of 120 employees of a
Q84: A market researcher obtains a sample of
Q107: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\frac { \sin x \cos
Q190: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\sec ^ { 2 }